Tankerman – PIC
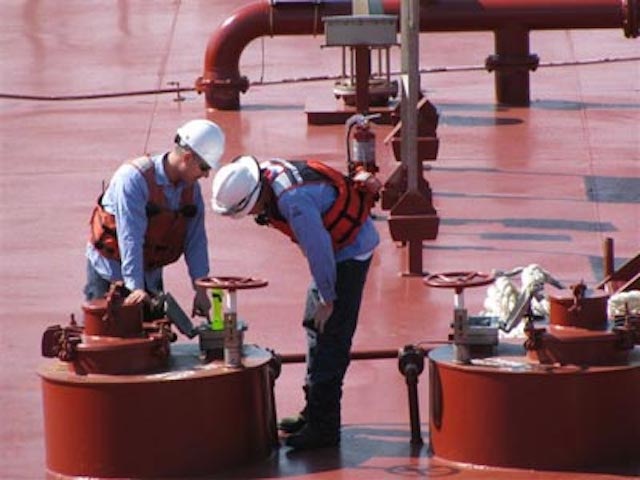

The Tankerman PIC (Person in Charge) is an endorsement that qualifies you to plan and oversee the cargo on a tank ship. To qualify for the Tankerman PIC endorsement, you’ll need: 90 days of service as a deck or engineering officer on a tankship or self-propelled tank vessel certified to carry DL or LG, OR.
| Tankerman Assistant Dangerous Liquids (TK01) | Tankerman Assistant Liquefied Gas (TK02) | ||
| Q456-Tankerman Assistant Dangerous Liquids | Q457-Tankerman Assistant Liquefied Gas | ||
| Basic knowledge of tankers | Basic knowledge of tankers | ||
| Basic knowledge of cargo operations | Basic knowledge of cargo operations | ||
| Basic knowledge of the physical properties of oil and chemicals | Basic knowledge of the physical properties of liquefied gases | ||
| Knowledge and understanding of tanker safety culture and safety management | Knowledge and understanding of tanker safety culture and safety management | ||
| Basic knowledge of the hazards associated with tanker operations | Basic knowledge of the hazards associated with tanker operations | ||
| Basic knowledge of hazard controls | Basic knowledge of hazard controls | ||
| Understanding of information on a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Understanding of information on a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | ||
| Function and proper use of gas-measuring instruments and similar equipment | Function and proper use of gas-measuring instruments and similar equipment | ||
| Proper use of safety equipment and protective devices | Proper use of safety equipment and protective devices | ||
| Basic knowledge of safe working practices and procedures in accordance with legislation and industry guidelines and personal shipboard safety relevant to oil and chemical tankers | Basic knowledge of safe working practices and procedures in accordance with legislation and industry guidelines and personal shipboard safety relevant to oil and chemical tankers | ||
| Basic knowledge of first aid with reference to a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | Basic knowledge of first aid with reference to a Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) | ||
| Basic knowledge of emergency procedures, including emergency shutdown | Basic knowledge of emergency procedures, including emergency shutdown | ||
| Basic knowledge of the effects of oil and chemical pollution on human and marine life | Basic knowledge of the effects of oil and chemical pollution on human and marine life | ||
| Basic knowledge of shipboard procedures to prevent pollution | Basic knowledge of shipboard procedures to prevent pollution | ||
| Basic knowledge of measures to be taken in the event of spillage | Basic knowledge of measures to be taken in the event of spillage |
Listed below is the table of contents of the questions on Tankerman – PIC as they appear in the online study. Click on the “Enter Online Study” link above to begin preparing for your exam. If you are studying for a United States Coast Guard Deck License exam which includes any of these modules, you should work through these questions until you are scoring 90% or better on all of them. Go to any of the following links to preview a cross section of the questions with correct answers and graphics on this subject that are included in our online study database.
From the pull down menu in the online study select from the following topics:
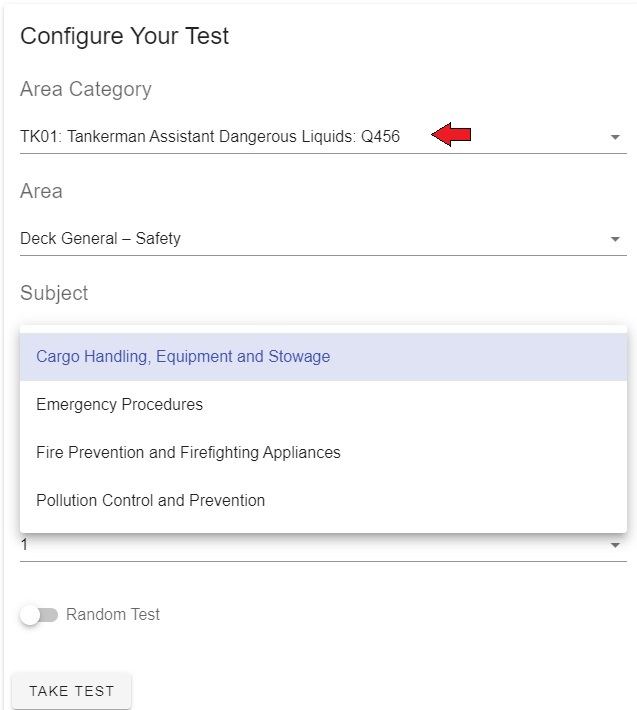
Course Topics for Tankerman – PIC
- General characteristics, compatibility, reaction, firefighting procedures, and safety precautions for the cargoes of:
- Bulk liquids defined as Dangerous Liquids in 46 CFR Part 13
- Bulk.liquefied gases & their vapors defined as Liquefied Gases in 46 CFR Part 13
- Physical phenomena of liquefied gas, including:
- Basic concept
- Compression and expansion
- Mechanism of heat transfer
- Potential hazards of liquefied gas, including:
- Chemical and physical properties
- Combustion characteristics
- Results of gas release to the atmosphere
- Health hazards (skin contact, inhalation, and ingestion)
- Control of flammability range with inert gas
- Thermal stress in structure and piping of vessel
- Cargo systems, including:
- Principles of containment systems
- Construction, materials, coating, & insulation of cargo tanks
- General arrangement of cargo tanks
- Venting and vapor-control systems
- Cargo-handling systems, including:
- Piping systems, valves, pumps, and expansion systems
- Operating characteristics
- Instrumentation systems,including:
- Cargo-level indicators
- Gas-detecting systems
- Temperature-monitoring systems, cargo
- Temperature-monitoring systems, hull
- Automatic-shutdown systems
- Auxiliary systems, including:
- Ventilation, inerting
- Valves, including:
- Quick-Cosing
- Remote-control
- Pneumatic
- Excess-flow
- Safety-relief
- Pressure-vacuum
- Heating-systems: cofferdams & ballast tanks
- Operations connected with the loading and discharging of cargo, including:
- Lining up the cargo and vapor-control systems
- Pre-transfer inspections and completion of the Declaration of Inspection
- Hooking up of cargo hose, loading arms, and grounding-strap
- Starting of liquid flow
- Calculation of loading rates
- Discussion of loading
- Ballasting and deballasting
- Topping off of the cargo tanks
- Discussion of discharging
- Stripping of the cargo tanks
- Monitoring of transfers
- Gauging of cargo tanks
- Disconnecting of cargo hoses or loading arms
- Cargo-tank-cleaning procedures and precautions
- Operating procedures and sequence for:
- Inerting of cargo tanks and void spaces
- Cooldown and warmup of cargo tanks
- Gas-freeing
- Loaded or ballasted voyages
- Testing of cargo-tank atmospheres for oxygen & cargo vapor
- Stability and stress considerations connected with loading and discharging of cargo
- Loadline, draft, and trim
- Disposal of boil-off, including:
- System design
- Safety features
- Stability-letter requirements
- Emergency procedures, including notice to appropriate authorities, for:
- Fire
- Collision
- Grounding
- Equipment failure
- Leaks and spills
- Structural failure
- Emergency discharge of cargo
- Entering cargo tanks
- Emergency shutdown of cargo-handling
- Emergency systems for closing cargo tanks
- Rules 4 regulations (international and Federal, for all tank vessels) on conducting operations and preventing pollution
- Pollution prevention, including:
- Procedures to prevent air and water pollution
- Measures to take in event of spillage .. .. _..
- Danger from drift of vapor cloud
- Terminology for tankships carrying oil and chemicals
- Terminology for tank barges carrying oil and chemicals
- Terminology for tankships carrying liquefied gases
- Terminology for tank barges carrying liquefied gases
- Principles & procedures of crude-oil-washing (COW) systems, including:
- Purpose
- Equipment and design
- Operations
- Safety precautions
- Maintenance of plant and equipment
- Principles & procedures of the inert-gas systems (IGSs), including:
- Purpose
- Equipment and design
- Operations
- Safety precautions
- Maintenance of plant and equipment
- Principles & procedures of vapor-control systems, including:
- Purpose
- Principles
- Coast Guard regulations
- Hazards
- Active system components
- Passive system components
- Operating procedures, including:
- Testing and inspection requirements
- Pre-transfer procedures
- Connecting sequence
- Start-up sequence
- Normal operations
- Emergency procedures
- Cargo-hazard-information systems
- Safe entry into confined spaces, including:
- Testing tank atmospheres for oxygen & hydrocarbon vapors
- Definition and hazards of confined spaces
- Cargo tanks and pumprooms
- Evaluation and assessment of risks and hazards
- Safety precautions and procedures
- Personnel protective equipment (PPE) and clothing
- Maintenance of PPE
- Dangers of skin contact
- Electricity and static electricity—hazards and precautions
- Emergency procedures
- Federal regulations, national standards & industry guidelines
- Inspections by marine chemists & competent persons, including hot-work permits & procedures
- Vessel response plans:
- Purpose, content, and location of information
- Procedures for notice and mitigation of spills
- Geographic-specific appendices
- Vessel-specific appendices
- Emergency-action checklist
Firefighting and Emergency Procedures
- Elements of fire (Fire triangle):
- Fuel
- Source of ignition
- Oxygen
- Ignition sources (general):
- Chemical
- Biological
- Physical
- Ignition sources applicable to barges
- Definitions of flammability and combustibility:
- Flammability
- Ignition point
- Burning temperature
- Burning speed
- Thermal value
- Lower flammable limit
- Upper flammable limit
- Flammable range
- Inerting
- Static electricity
- Flash point
- Auto-ignition
- Spread of fire:
- By radiation
- By convection *
- By conduction
- Reactivity
- Fire classifications and applicable extinguishing agents
- Main causes of fires:
- Oil leakage
- Smoking
- Overheating pumps
- Galley appliances
- Spontaneous ignition
- Hot work –
- Electrical apparatus
- Reaction, self-heating, and auto-ignition
- Main causes of fires:
- Fire prevention:
- General
- Fire hazards of DL and LG
- Fire detection:
- Fire- and smoke-detection systems
- Automatic fire alarms
- Firefighting equipment:
- Fire mains, hydrants
- International shore-connection
- Smothering-installations, carbon dioxide (CO2), foam
- Halogenated hydrocarbons
- Pressure-water spray system in special-category spaces
- Automatic sprinkler system
- Emergency fire pump, emergency generator
- Chemical-powder applicants
- General outline of required and mobile apparatus
- Fireman’s outfit, personal equipment
- Breathing apparatus
- Resuscitation apparatus
- Smoke helmet or mask
- Fireproof life-line and harness
- Fire hose, nozzles, connections, and fire axes
- Fire blankets
- Portable fire extinguishers
- Limitations of portable and semiportable extinguishers
- Emergency procedures:
- Arrangements:
- Escape routes
- Means of gas-freeing tanks
- Class A, B, and C divisions
- Inert-gas system
- Ship firefighting organization:
- General alarms
- Fire-control plans, muster stations, and duties
- Communications
- Periodic shipboard drills
- Patrol system
- Basic firefighting techniques:
- Sounding alarm
- Locating and isolating fires …
- Stopping leakage of cargo
- Jettisoning ..
- Inhibiting ….
- Cooling
- Smothering
- Sizing up situation _
- Locating information on cargo
- Extinguishing
- Extinguishing with portable units
- Setting reflash watch
- Using additional personnel
- Firefighting extinguishing-agents:
- Water (solid jet, spray, fog, and flooding)
- Foam (high, medium and low expansion)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Halon
- Aqueous-film-forming foam (AFFF)
- Dry chemicals
- Use of extinguisher on:
- Flammable and combustible liquids
- Manifold-flange fire
- Drip-pan fire
- Pump fire
- Drills for typical fires on barges
- Arrangements:
- Field exercises:
- Extinguish small fires using portable extinguishers:
- Electrical
- Manifold-flange
- Drip-pan
- Pump
- Use self-contained breathing apparatus
- Extinguish extensive fires with water
- Extinguish fires with foam, or chemical –
- Fight fire in smoke-filled enclosed space wearing SCBA
- Extinguish fire with water fog in an enclosed space with heavy smoke
- Extinguish oil fire with fog applicator and spray nozzles, dry-chemical, or foam applicators
- Effect a rescue in a smoke-filled space while wearing breathing apparatus
- Extinguish small fires using portable extinguishers:
